Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
PET scanning is a gamma-based imaging technique that allows doctors to detect early signs of cancer, brain disorders and heart diseases by identifying changes in organs and tissues at cellular level. In a PET scan, the patient is injected with a radioactive substance and placed on a flat table that moves into a donut-shaped housing called gantry.
The gantry of a PET system contains several gamma ray detectors that require very precise temperature control to one another in order to generate a proper image. If one detector fails it will have a significant impact on the final image result.
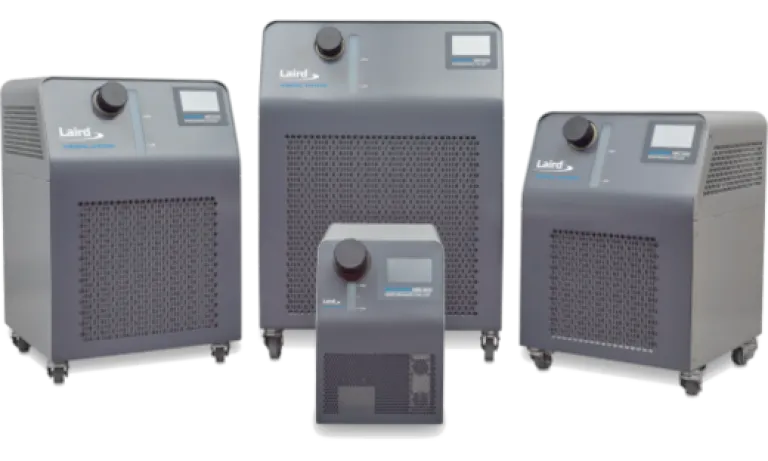
Liquid Cooling Solutions
With the ability to cool well below ambient at a temperature accuracy of ±0.1°C the Nextreme Series supports cooling needs of PET scanning systems. This is a new generation recirculating chiller offering lower noise and reduced energy consumption compared to previous models.
Related Content